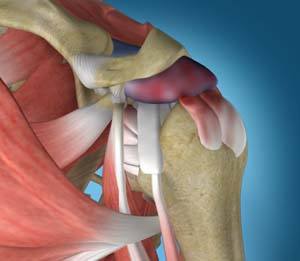
Shoulder Anatomy
The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint. The ball-shaped end of the upper arm bone (humerus) fits neatly into a socket, called the glenoid, which is part of the shoulder blade or scapula.
What is Shoulder Impingement?
Shoulder impingement is the inflammation of the tendons of the shoulder joint. It is one of the most common causes of pain in the shoulder. Shoulder impingement is also called bursitis, swimmer’s shoulder, tennis shoulder or rotator cuff tendinitis.
Causes of Shoulder Impingement
Impingement results in the young and middle-aged who engage in physical activities that require repeated overhead arm movements. The pain may be due to bursitis (inflammation of the bursa) overlying the rotator cuff or tendonitis of the cuff itself. In some circumstances, a partial tear of the rotator cuff may cause impingement pain.
Symptoms of Shoulder Impingement
Individuals with shoulder impingement may experience severe pain at rest and during activities, weakness of the arm and difficulty in raising the hand overhead.
Diagnosis of Shoulder Impingement
Diagnosis involves a physical examination by your doctor, where your doctor checks for the possible range of movements with the affected shoulder. X-rays and MRI scans may be ordered to view the injury and inflammation.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Impingement
Conservative Treatment Options for Shoulder Impingement
Shoulder impingement can be treated with rest, ice packs, anti-inflammatory drugs and avoiding activities involving the shoulder. Physical therapy may be advised to strengthen the muscles and steroid injections may be administered if pain persists.
Surgery for Shoulder Impingement
Arthroscopic surgery is recommended if the rotator cuff tendons are torn and to remove the bony spurs.













